The Problem
Surprise medical bills—also known as “balance billing”—have long been one of the most pressing affordability concerns facing American families. Historically, most states allowed doctors to bill patients for any balance remaining after their health insurance paid its share. These charges were particularly devastating when out-of-network providers—who had no contractual rate agreements with insurers—billed patients for the full cost of care.
Today, with the No Surprises Act in place, patients are protected from most surprise medical bills. But new challenges have emerged. Certain private equity–backed providers and profit-focused intermediaries are now exploiting the law’s arbitration process as a business model to maximize revenue.
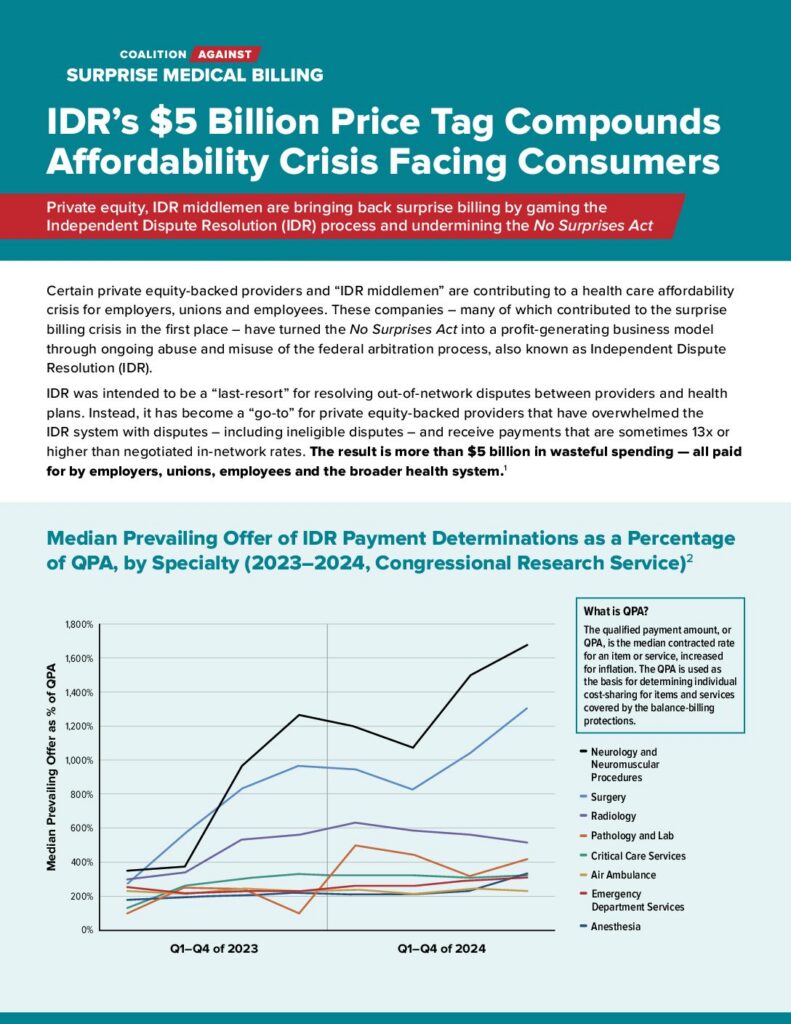
Instead of serving as a last-resort mechanism for payment disputes, the independent dispute resolution (IDR) process has been flooded with claims. Millions of cases have been filed since the law’s passage—far exceeding government projections—many of which are ineligible or inflated. This surge has created costly bottlenecks, slowed down legitimate dispute resolution, and burdened both health plans and employers with unnecessary administrative fees.
What’s more, data show that providers are prevailing more frequently in arbitration, and when they win, their awards are often many times higher than typical in-network or Medicare rates. This not only drives up direct costs for health plans but also raises premiums and out-of-pocket expenses for American families. Meanwhile, IDR entities are not required to provide full explanations of their decisions, and the law lacks a clear appeals process—leaving limited accountability or oversight.
Latest News
Recent Report Details How Arbitration Could Become “Permanent Cost Escalator”
When Congress passed the No Surprises Act, the goal was clear: protect patients from unexpected out-of-network medical bills. The law has largely succeeded in that regard, shielding patients from most surprise bills — especially large balance bills tied to emergency...
Abuse & Misuse of Arbitration Fueling Affordability Crisis
The evidence of certain providers' routine abuse and misuse of the No Surprises Act’s Independent Dispute Resolution (IDR) process, also known as arbitration, has been overwhelming. Recent lawsuits reveal repeated and persistent patterns of fraudulent IDR submissions,...
Latest IDR Data Confirms Ongoing Abuse by Private Equity-Backed Providers and IDR Middlemen
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) just released new data from the first half of 2025 on the No Surprises Act’s Independent Dispute Resolution (IDR) process, and the numbers are staggering. Nearly 1.2 million disputes were filed in just six months,...